Intestinal
Intestinal dysbiosis refers to an imbalance in the natural intestinal flora in which harmful bacteria get out of hand and can impair health.
The prevalence of intestinal dysbiosis is estimated at 5-20% worldwide. However, when you read that it is estimated that 10-20% of the population here already suffers from irritable bowel syndrome, then I would tend to think that at least 20% of the population suffers from dysbiosis. Especially as there are also studies from Germany and Belgium that have shown that 70% of the population suffer from gastrointestinal complaints at least once a year.
Another interesting figure I found is from the year 2023. The Swiss Federal Office of Public Health says that 19% of the Swiss population will have taken antibiotics in 2022.
Another revealing figure comes from ANRESIS, the Swiss Center for Antibiotic Resistance, which is run by the Institute for Infectious Diseases (IFIK) at the University of Bern. It says that more than 5.6 million packs of antibiotics were sold in Switzerland in 2023.
If you now look at the diverse effects of intestinal dysbiosis, I suspect that it is far more common than in just 20% of the population.
These are just 7 of many more effects. If you make an effort and dig a little deeper, you can find many more. For example, allergies, respiratory diseases, ADHD and many more.
The exact effects of dysbiosis can vary greatly from person to person and depend on various factors such as the extent of the imbalance and the general health of the person affected. Nevertheless, it is impressive how many people come to mind who fall into this category.
Arktibiotic Akut: https://shop.arktisbiopharma.ch/arktibiotic-akut-akut-30-kapseln/100177
Arktibiotic Premium: https://shop.arktisbiopharma.ch/arktibiotic-premium-premium-60g/100136
BALLAST-FRIENDLY
Table from Biovis: https://www.biovis.eu/wp-content/uploads/Ernaehrungsinfo-10.pdf
GUT-FRIENDLY
21-day detox and intermittent fasting program: https://www.arktisbiopharma.ch/upgraders
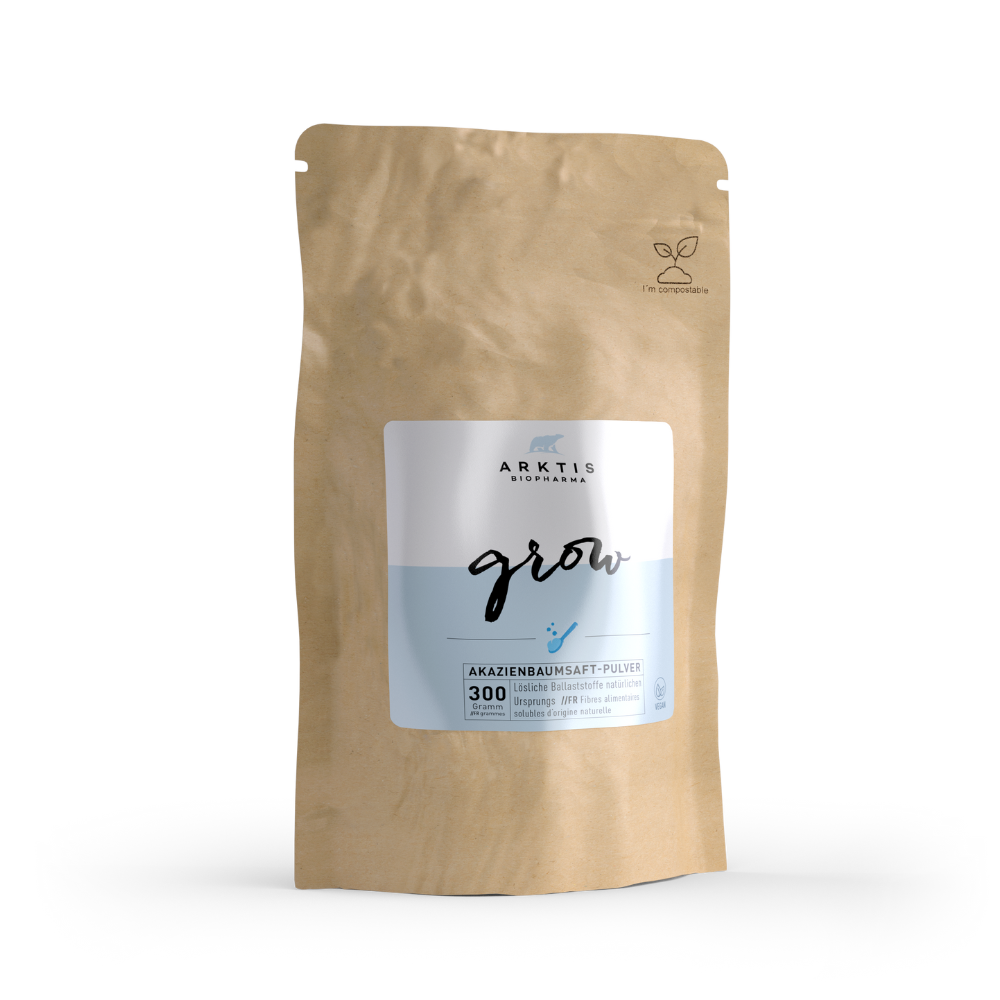
Arktis Grow acacia fibres: https://shop.arktisbiopharma.ch/akazienfasern-pulver-ballaststoff-grow-300g-beutel-doypack/120231
Do you want to know whether you have pathogenic or potentially pathogenic bacteria or parasites? Or even know the extent of your dysbiosis? Then have your dysbiosis index determined!
Microbiome analysis: https://shop.arktisbiopharma.ch/leaky-gut-analyse/B-103
https://shop.arktisbiopharma.ch/mikrobiomanalyse-mit-audio-besprechung/B-100-900002
post(at)arktisbiopharma.ch; Tel: +41 61 311 77 11
Enter the voucher code podcast15 before you complete your order.
Arktis BioPharma Shop Switzerland
Arktis BioPharma Shop Germany
Then subscribe to the Darmglück podcast in your favorite podcast app and follow us on social media.
Here are the links to my podcast in the most popular apps and to Arktis BioPharma on social media









dysbiosis an underestimated health problem
Intestinal dysbiosis refers to an imbalance in the natural intestinal flora in which harmful bacteria get out of hand and can impair health.
The prevalence of intestinal dysbiosis is estimated at 5-20% worldwide. However, when you read that it is estimated that 10-20% of the population here already suffers from irritable bowel syndrome, then I would tend to think that at least 20% of the population suffers from dysbiosis. Especially as there are also studies from Germany and Belgium that have shown that 70% of the population suffer from gastrointestinal complaints at least once a year.
Another interesting figure I found is from the year 2023. The Swiss Federal Office of Public Health says that 19% of the Swiss population will have taken antibiotics in 2022.
Another revealing figure comes from ANRESIS, the Swiss Center for Antibiotic Resistance, which is run by the Institute for Infectious Diseases (IFIK) at the University of Bern. It says that more than 5.6 million packs of antibiotics were sold in Switzerland in 2023.
If you now look at the diverse effects of intestinal dysbiosis, I suspect that it is far more common than in just 20% of the population.
Key takeaways
- Gut dysbiosis and prevalence: Gut dysbiosis is more common than suspected, with far-reaching effects on health
- Effects of gut dysbiosis: A wide range of symptoms such as digestive problems, immunological weaknesses, inflammatory diseases and psychological stress can occur
- Causes of gut dysbiosis: factors such as antibiotic use, unbalanced diet, chronic stress and medication have a negative impact on the microbiome
- Health data: Statistics on antibiotic use and sales figures in Switzerland provide an insight into how gut health and medication are handled
- Individual influencing factors: Genetic predisposition, environmental factors and lifestyle habits play a role in the development of intestinal dysbiosis
The consequences of dysbiosis are extremely varied
- Digestive problems: Symptoms such as flatulence, abdominal pain, diarrhea or constipation often occur. These symptoms result from the altered bacterial composition in the gut.
- Impairment of the immune system: As a large part of the immune system is located in the intestine, dysbiosis can weaken the immune system and increase susceptibility to infections.
- Inflammatory bowel diseases: A disturbed microbiome can promote the development of inflammatory bowel diseases such as irritable bowel syndrome or chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
- Systemic inflammation: Dysbiosis can lead to increased permeability of the intestinal barrier, allowing toxins to enter the bloodstream and trigger systemic inflammation.
- Metabolic disorders: There is evidence that an imbalance of the intestinal flora is linked to metabolic diseases such as obesity and type 2 diabetes.
- Skin problems: Skin conditions such as acne or eczema can be affected by impaired gut flora.
- Mental impairments: Via the gut-brain axis, dysbiosis can also have an impact on the psyche and contribute to symptoms such as anxiety or depression.
These are just 7 of many more effects. If you make an effort and dig a little deeper, you can find many more. For example, allergies, respiratory diseases, ADHD and many more.
The exact effects of dysbiosis can vary greatly from person to person and depend on various factors such as the extent of the imbalance and the general health of the person affected. Nevertheless, it is impressive how many people come to mind who fall into this category.
- Antibiotic use: Antibiotics can alter up to 90% of gut bacteria by killing not only harmful but also beneficial bacteria. This can allow pathogenic germs to multiply
- Unbalanced diet: A diet high in sugar and saturated fat can promote the growth of unfavorable bacteria.
- Chronic stress: Prolonged stress can have a negative impact on the composition of the intestinal flora.
- Lack of fiber: Diets low in fiber can lead to a reduced diversity of gut bacteria. I found a figure from 2014, when the average daily fiber intake in Switzerland was around 20g. However, 30g is recommended for a healthy intestinal flora. At least! In the past, people even ate 100g of fiber per day.
Biovis laboratory has a helpful table showing how much fiber is contained in which foods: https: //www.biovis.eu/wp-content/uploads/Ernaehrungsinfo-10.pdf - Infections of the gastrointestinal tract: Bacterial, viral or parasitic infections can disrupt the balance of the intestinal flora.
- Long-term use of medication: In addition to antibiotics, other medications such as proton pump inhibitors (acid blockers) or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (i.e. generally painkillers that many people take several times a year, such as ibuprofen) can also affect the intestinal flora, for example by damaging the intestinal mucosa.
- Hormonal changes: Pregnancy, menopause or taking hormonal contraceptives can affect the gut flora.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to pollutants or excessive hygiene (use of disinfectants) can change the microbiome.
- Genetic predisposition: Genetic factors can increase susceptibility to dysbiosis.
- Alcohol and tobacco consumption: Both alcohol and smoking can affect the balance of the intestinal flora; nicotine, the primary active substance in tobacco smoke, can change the composition of the intestinal bacteria by increasing the pH value in the intestine, reducing the number of certain types of bacteria such as Bacteroides and increasing others such as Firmicutes and Proteobacteria. In addition, substances contained in tobacco smoke such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, heavy metals and toxic gases can affect the microbiome, and alcohol consumption can damage the intestinal barrier and negatively influence the intestinal flora. Studies have shown that regular alcohol consumption can lead to damage to the intestinal barrier.
LINKS
TO ANTIBIOBIOTICS
Arktibiotic Akut: https://shop.arktisbiopharma.ch/arktibiotic-akut-akut-30-kapseln/100177
Arktibiotic Premium: https://shop.arktisbiopharma.ch/arktibiotic-premium-premium-60g/100136
BALLAST-FRIENDLY
NUTRITION
Table from Biovis: https://www.biovis.eu/wp-content/uploads/Ernaehrungsinfo-10.pdf
GUT-FRIENDLY
NUTRITION
21-day detox and intermittent fasting program: https://www.arktisbiopharma.ch/upgraders
Arktis Grow acacia fibres: https://shop.arktisbiopharma.ch/akazienfasern-pulver-ballaststoff-grow-300g-beutel-doypack/120231
Do you want to know whether you have pathogenic or potentially pathogenic bacteria or parasites? Or even know the extent of your dysbiosis? Then have your dysbiosis index determined!
Microbiome analysis: https://shop.arktisbiopharma.ch/leaky-gut-analyse/B-103
https://shop.arktisbiopharma.ch/mikrobiomanalyse-mit-audio-besprechung/B-100-900002
CONTACT MILENA
post(at)arktisbiopharma.ch; Tel: +41 61 311 77 11
As a podcast listener, you will receive a discount on our products
A 15% discount on your first purchase (applicable once, only on products not already discounted). The voucher code is valid in both Arktis BioPharma stores in Switzerland and Germany.Enter the voucher code podcast15 before you complete your order.
Arktis BioPharma Shop Switzerland
Arktis BioPharma Shop Germany
Subscribe to the Darmglück podcast and follow us on social media
You don't want to miss any future episodes and/or want to stay up to date?Then subscribe to the Darmglück podcast in your favorite podcast app and follow us on social media.
Here are the links to my podcast in the most popular apps and to Arktis BioPharma on social media